How do cashew trees germinate and grow? Stages of cashew tree growth

Mục lục
Cashew is a perennial industrial tree, with a growth and development period of up to 40 years. Cashew trees germinate so they produce cashew seeds. So how do cashews grow? To become a mature cashew tree with a high yield, how do cashews germinate and grow? What are the stages of cashew tree development? What are the characteristics of cashew trees?... Let's learn and analyze more in the article below.

How does a cashew tree germinate and grow?
Germination is the process by which a new plant develops from a seed. The most common example of germination is a seedling emerging from the seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm. However, the development of daughter spores from a mother spore, such as the development of mycelium from fungal spores, is also considered germination. Therefore, germination can be understood in a general sense as anything that becomes larger from a small entity or part of a living organism and is a method that is often used in many seed development projects.
The process of germination and growth of a cashew tree takes place through the following stages:
The process of germination and growth of a cashew tree takes place through the following stages:
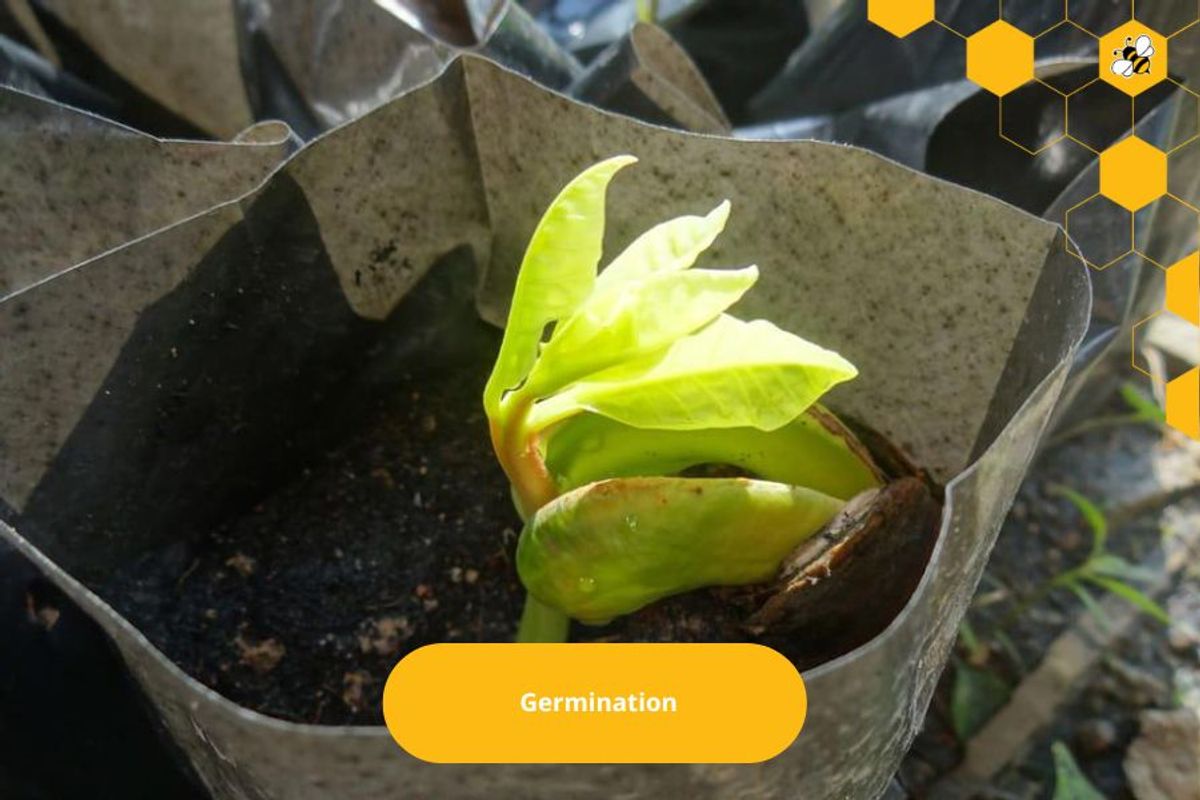
Germination
The cashew seed is planted in moist soil with suitable humidity and temperature conditions.
After a few days, the cashew seed will swell due to the absorption of water.
The seed coat cracks open so that the root can penetrate the soil.
From around the rootstock, many small roots will grow.
After a few days, the cashew seed will swell due to the absorption of water.
The seed coat cracks open so that the root can penetrate the soil.
From around the rootstock, many small roots will grow.

Seedlings
Seedlings develop stems and branches.
The cashew tree trunk is short, the branches are long, and the roots grow deep into the soil.
The leaves of the cashew tree grow alternately, are green, and have a mild fragrance.
The cashew tree trunk is short, the branches are long, and the roots grow deep into the soil.
The leaves of the cashew tree grow alternately, are green, and have a mild fragrance.
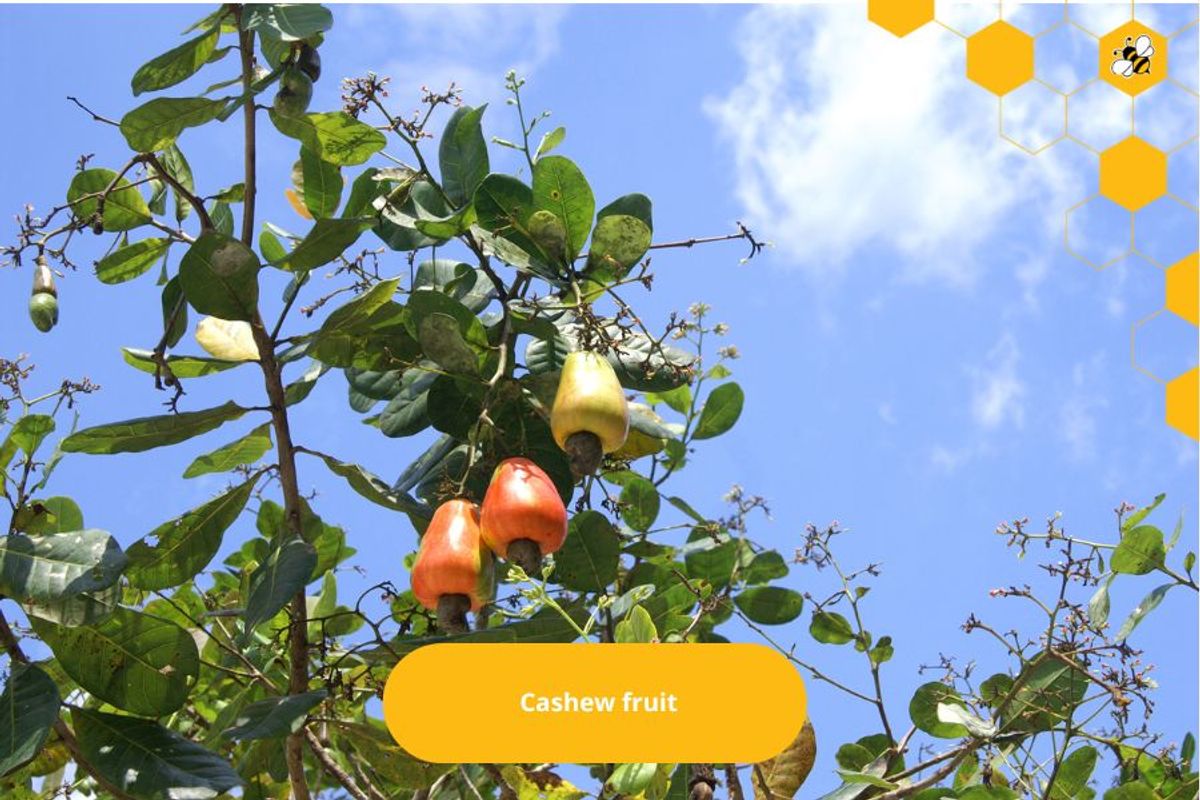
Cashew fruit
Cashew fruit has a hard shell, sunken eyes, and a pear-shaped stalk.
The cashew nut is inside the fruit and is surrounded by a hard shell.
The cashew nut is inside the fruit and is surrounded by a hard shell.

Growth and Lifespan
Cashew trees can live up to 40-50 years.
They usually produce the most consistent yields between 10 and 20 years after planting.
Water is essential for germination. Mature seeds are very dry and need to absorb a significant amount of water before cell growth can begin. Most seeds need enough water to moisten them but not to saturate them. The absorption of water by the seed is called imbibition, which causes the seed coat to swell and break. Once the seed has formed, most plants will store a reserve of “food” with the seed, such as protein, starch, or oil.
They usually produce the most consistent yields between 10 and 20 years after planting.
Water is essential for germination. Mature seeds are very dry and need to absorb a significant amount of water before cell growth can begin. Most seeds need enough water to moisten them but not to saturate them. The absorption of water by the seed is called imbibition, which causes the seed coat to swell and break. Once the seed has formed, most plants will store a reserve of “food” with the seed, such as protein, starch, or oil.

Stages of Cashew Tree Growth from Sprouting to Fruiting
The growth cycle of a cashew tree includes the following stages:
Germination: This is the first stage in the growth cycle of a tree. After the seed is placed in a suitable environment and receives enough water and nutrients, the tree begins to develop roots and stems. The roots help the tree absorb water and nutrients, while the stems carry nutrients from the roots to other parts of the tree. Leaves also begin to develop so that the tree can photosynthesize and continue to grow.
Growth and Development: After the germination stage, the tree continues to grow in size. It produces new branches and leaves to continue the process of photosynthesis and absorption of nutrients. The tree needs enough water and light to grow during this stage.
Reproduction: This stage marks the development of flowers and fruits. The tree faces challenges from the environment such as insects, diseases, and natural disasters. Caring for the tree during this stage is very important to ensure that the tree is strong and healthy. Flowering and Fruiting:
Flowering (R1): The plant begins to flower on any node.
Full flowering (R2): Flowers will open on one of the two highest nodes on the main stem of the plant, with fully developed leaves.
Start of fruiting (R3): The fruit is about 0.5cm long on one of the four highest nodes on the main stem, with fully developed leaves.
Seed dispersal: The plant eventually produces seeds and disperses them into the surrounding environment.
Germination: This is the first stage in the growth cycle of a tree. After the seed is placed in a suitable environment and receives enough water and nutrients, the tree begins to develop roots and stems. The roots help the tree absorb water and nutrients, while the stems carry nutrients from the roots to other parts of the tree. Leaves also begin to develop so that the tree can photosynthesize and continue to grow.
Growth and Development: After the germination stage, the tree continues to grow in size. It produces new branches and leaves to continue the process of photosynthesis and absorption of nutrients. The tree needs enough water and light to grow during this stage.
Reproduction: This stage marks the development of flowers and fruits. The tree faces challenges from the environment such as insects, diseases, and natural disasters. Caring for the tree during this stage is very important to ensure that the tree is strong and healthy. Flowering and Fruiting:
Flowering (R1): The plant begins to flower on any node.
Full flowering (R2): Flowers will open on one of the two highest nodes on the main stem of the plant, with fully developed leaves.
Start of fruiting (R3): The fruit is about 0.5cm long on one of the four highest nodes on the main stem, with fully developed leaves.
Seed dispersal: The plant eventually produces seeds and disperses them into the surrounding environment.

So you know about the development process of the cashew tree from sprouting to fruiting.
Some outstanding features of the cashew tree
The cashew tree (also known as the cashew tree) has some outstanding features:
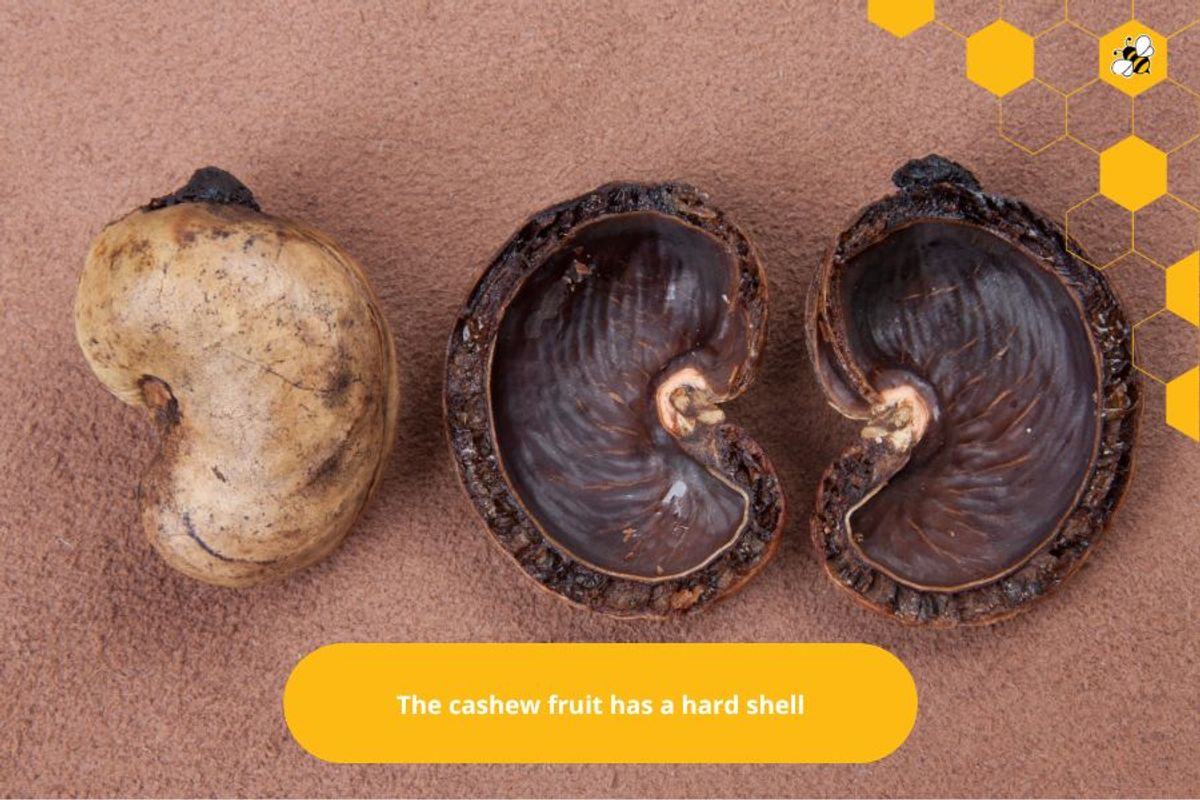
Cashew fruit
The cashew fruit has a hard shell, concave eyes, and a pear-shaped stalk. Inside the shell is the cashew nut, covered by a thin, brown shell. Cashew nuts are delicious and have high nutritional value, containing lots of fat, protein, vitamins, and minerals.

Leaves
The leaves of the cashew tree grow alternately, are silvery, turn white, and have a mild aroma. The leaves play an important role in photosynthesis, helping the tree to create energy from sunlight.
Shape: The cashew leaves are oval, with prominent veins and midribs. Each leaf ranges in size from 10 to 20 cm, and in width from 7 to 12 cm.
Color: When young, the cashew leaves are purplish green at the top and lighter green at the bottom. The leaves have a hard texture and a distinctive aromatic flavor.
Nutritional value: Cashew leaves are rich in antioxidants and have antifungal, antiparasitic, antibacterial, antiseptic, and anti-inflammatory properties. In addition, cashew leaves also contain vitamin B and vitamin C, provide iron and calcium, as well as other minerals such as zinc, magnesium, phosphorus, manganese, sodium, and potassium.
Shape: The cashew leaves are oval, with prominent veins and midribs. Each leaf ranges in size from 10 to 20 cm, and in width from 7 to 12 cm.
Color: When young, the cashew leaves are purplish green at the top and lighter green at the bottom. The leaves have a hard texture and a distinctive aromatic flavor.
Nutritional value: Cashew leaves are rich in antioxidants and have antifungal, antiparasitic, antibacterial, antiseptic, and anti-inflammatory properties. In addition, cashew leaves also contain vitamin B and vitamin C, provide iron and calcium, as well as other minerals such as zinc, magnesium, phosphorus, manganese, sodium, and potassium.

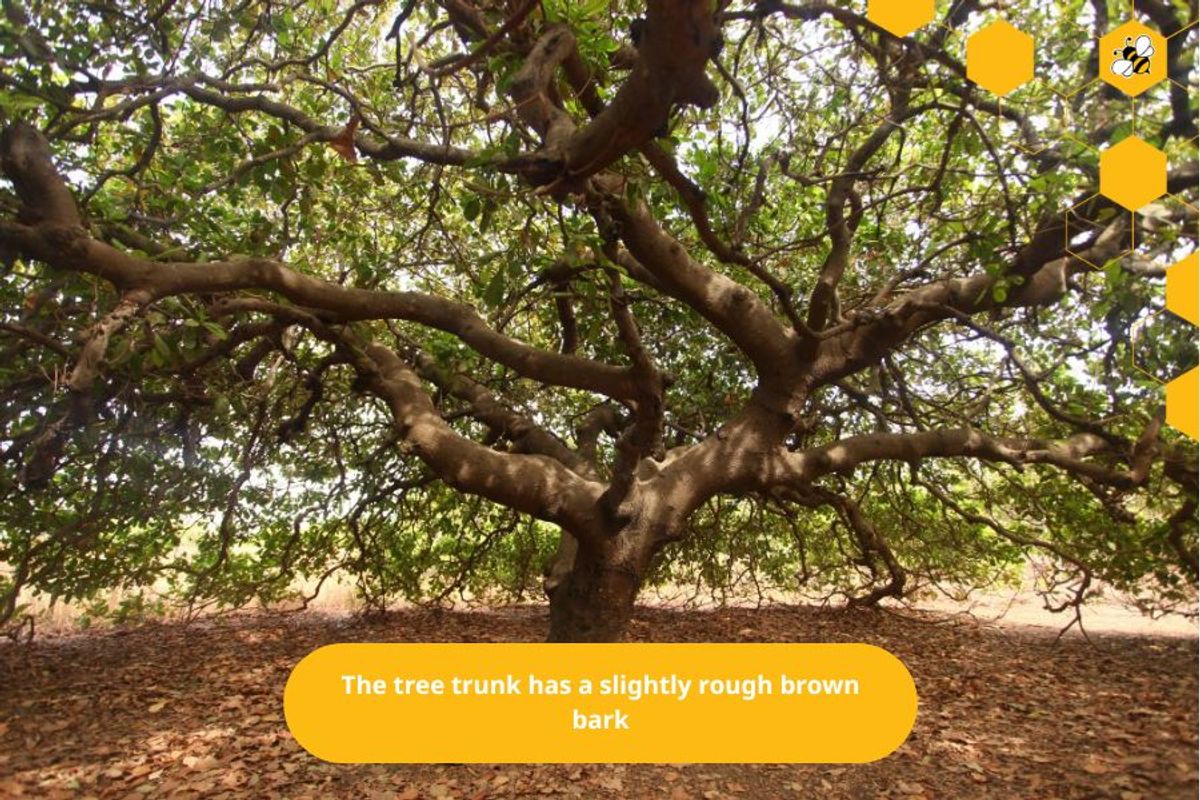
Trunk
Cashew trees are usually about 3m to 9m tall. The trunk may or may not be branched, depending on the type of tree and environmental conditions. Small branches often grow down to the ground. The trunk has brown, slightly rough bark.

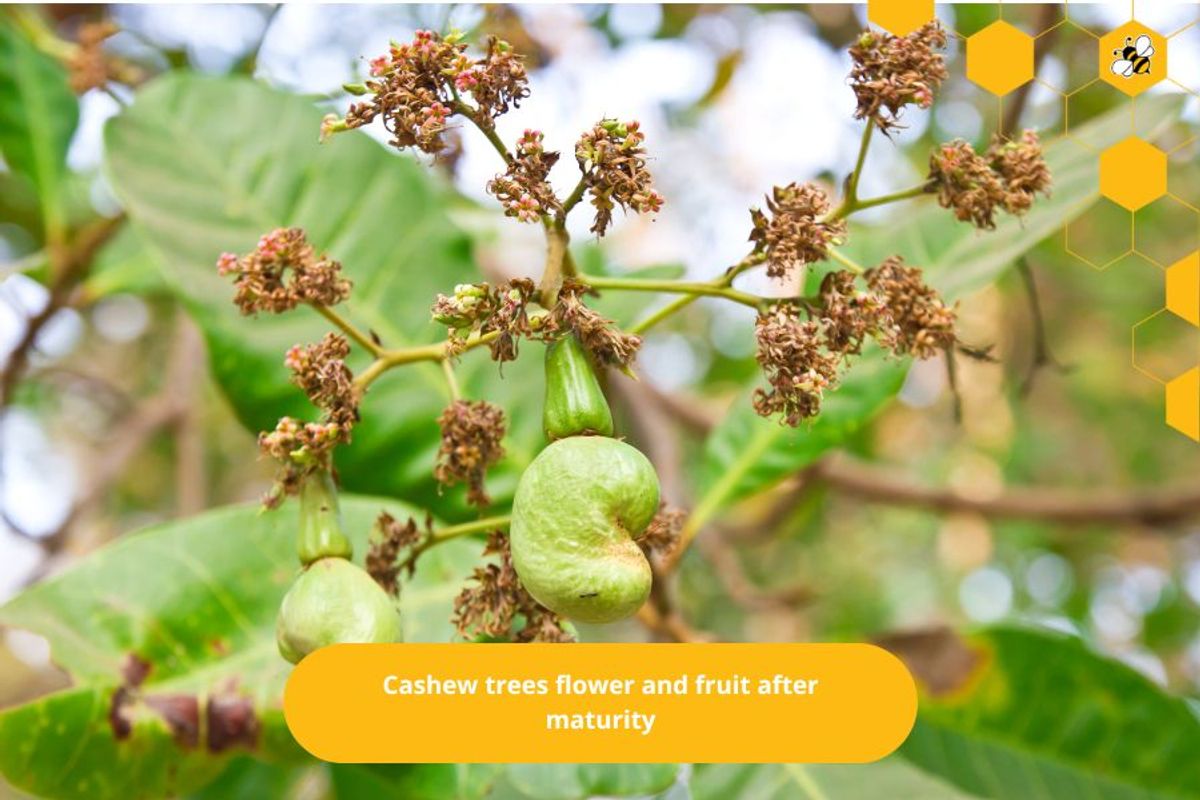
Flowers and fruits
Cashew trees flower and fruit after maturity. The flowers of the cashew tree bloom in small clusters, are white in color, and grow at the ends of branches. Cashew nuts develop from the flowers, and have a characteristic shape and sweet taste.

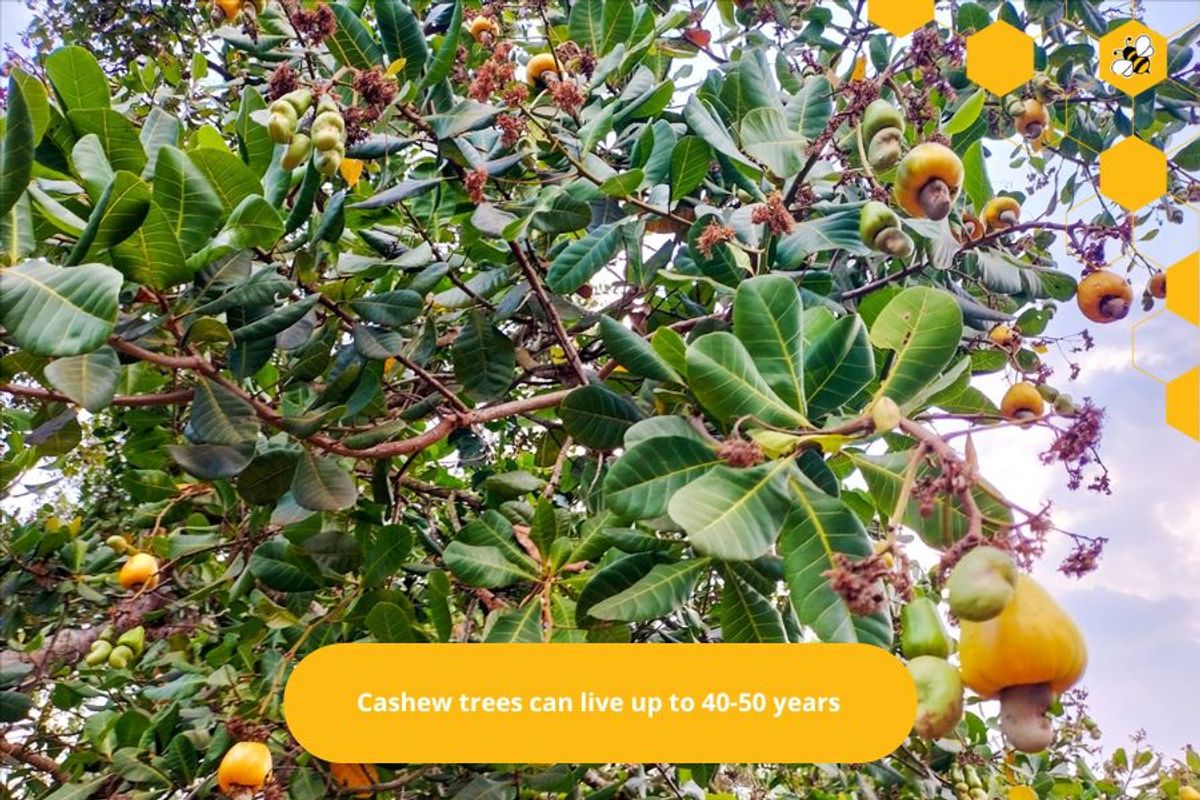
Yield and lifespan
Cashew trees have a lifespan of up to 40-50 years, and usually give stable yields for 10 to 20 years after planting.
In short, the cashew tree is not only a tree with high economic value but also has unique and attractive characteristics in the process of development and growth.

Summary
The cashew tree is not only a tree with high economic value but also has unique characteristics in the process of development and growth. From the germination of the cashew seed, and the development of the sapling, to the cashew fruit and cashew apple, each stage contributes to the richness and attractiveness of this tree. Enjoy the cashew nuts and cashew fruits with caution and be grateful for the diversity of nature.