What do cashews look like? Characteristics of cashews
Mục lục
Among all nuts, Cashews are foods that are very rich in nutrients and provide a lot of energy for the body. Currently, cashews are becoming more and more popular not only because of their delicious, fatty flavor but also because of their nutritional value and the great benefits that cashews bring to human health.

What do cashews look like?
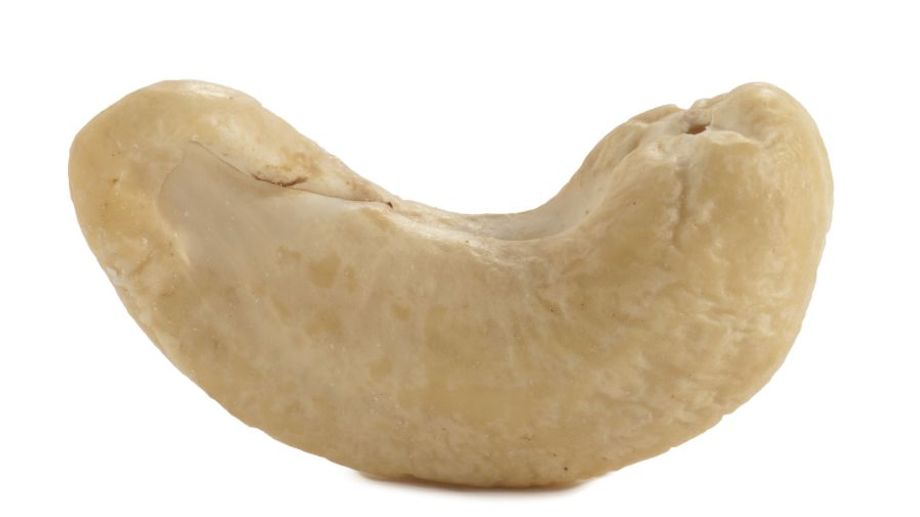
Cashews are shaped like beans. Inside the seeds are edible flesh. After removing the bark and phenolic resin that is toxic to the skin, they are suitable for human consumption. Cashews in their natural state are almost off-white in color, but when fried or roasted, they burn, turning a darker, slightly darker brown.
Cashew trees are usually about 3m to 9m tall. The leaves grow alternately, are silvery, turn white, and have a light aroma. Cashew nuts have a hard shell, do not open by themselves, have sunken eyes, and the fruit stalk swells into a pear shape.
Cashew trees are usually about 3m to 9m tall. The leaves grow alternately, are silvery, turn white, and have a light aroma. Cashew nuts have a hard shell, do not open by themselves, have sunken eyes, and the fruit stalk swells into a pear shape.

Cashews have a unique shape and are usually divided into two parts:
The seed
This is an important part of the cashew fruit.
Cashews are shaped like chestnuts, but larger.
They are usually white or pale in color and taste sweet, sour, and astringent.
Cashews are packed with nutrients, including protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
Cashews are shaped like chestnuts, but larger.
They are usually white or pale in color and taste sweet, sour, and astringent.
Cashews are packed with nutrients, including protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
The outer shell
The outer shell of the cashew is a thin, gray or brown layer.
When the cashew fruit is ripe, the outer shell opens and reveals the seed inside. This outer shell is usually hard and inedible.
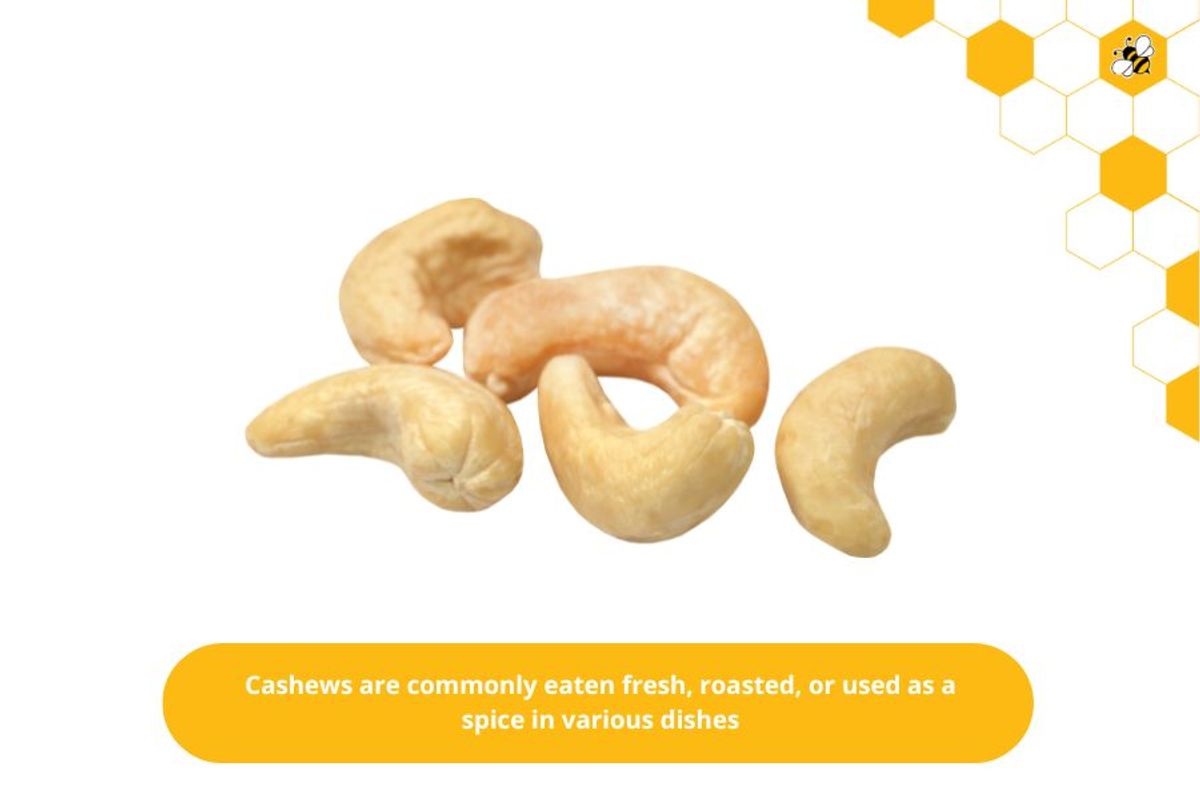
Cashews are often eaten fresh, roasted, or used as a spice in various dishes.
When the cashew fruit is ripe, the outer shell opens and reveals the seed inside. This outer shell is usually hard and inedible.
Cashews are often eaten fresh, roasted, or used as a spice in various dishes.

Characteristics of Cashew Fruit
Cashew fruit (also known as cashew nut) is a fruit with a diverse and unique shape. Here is a description of the characteristics of cashew fruit:
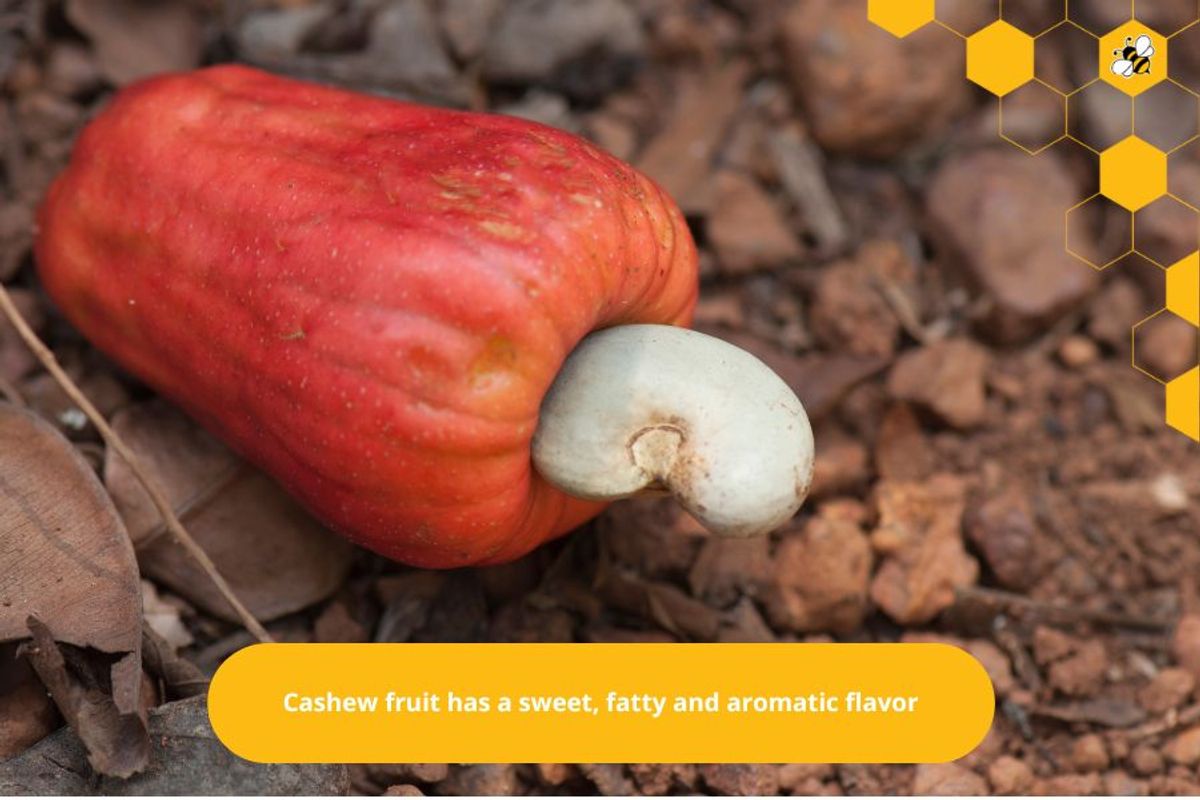
Shape and color: Cashew fruit can be pear-shaped, cylindrical, truncated cone, or even diamond-shaped. The color of cashew fruit varies from light yellow to bright red and may have green spots on the surface.
Outer shell: The outer shell of the cashew fruit is a thin, gray or brown layer. When the cashew fruit is ripe, the outer shell opens and reveals the seed inside. This outer shell is usually hard and inedible.
Cashew nut: This is an important part of the cashew fruit. Cashew nuts are shaped like chestnuts, but larger. They are usually white or pale in color and taste sweet, sour, and astringent. Cashew nuts contain many nutrients, including protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
Uses: Cashew nuts are used to make salted roasted cashews, cashew jam, cakes, and baked goods. In addition, cashews can also be eaten raw and are often used in bird's nest dishes, salads, and drinks.
Flavor and quality:
Cashews have a sweet, fatty, and aromatic flavor.
Cashews contain many nutrients such as protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Shape and color: Cashew fruit can be pear-shaped, cylindrical, truncated cone, or even diamond-shaped. The color of cashew fruit varies from light yellow to bright red and may have green spots on the surface.
Outer shell: The outer shell of the cashew fruit is a thin, gray or brown layer. When the cashew fruit is ripe, the outer shell opens and reveals the seed inside. This outer shell is usually hard and inedible.
Cashew nut: This is an important part of the cashew fruit. Cashew nuts are shaped like chestnuts, but larger. They are usually white or pale in color and taste sweet, sour, and astringent. Cashew nuts contain many nutrients, including protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
Uses: Cashew nuts are used to make salted roasted cashews, cashew jam, cakes, and baked goods. In addition, cashews can also be eaten raw and are often used in bird's nest dishes, salads, and drinks.
Flavor and quality:
Cashews have a sweet, fatty, and aromatic flavor.
Cashews contain many nutrients such as protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.

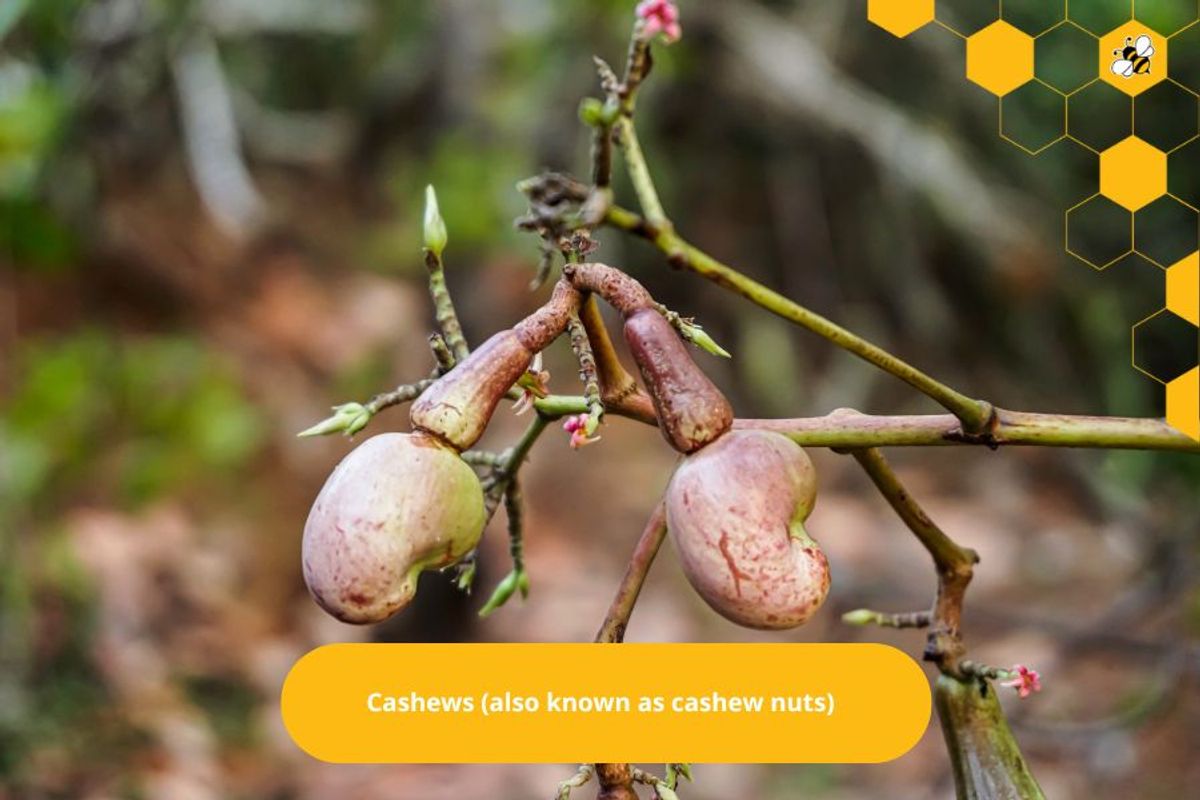
In addition, cashew trees are also grown in many different countries, including Vietnam, India, Nigeria, Indonesia, the Philippines, and many other places.
Characteristics of cashew nuts
Cashew nuts (also known as cashew nuts) have many interesting characteristics. Detailed description of cashew nuts:
Shape and color
Cashew fruits can be pear-shaped, cylindrical, truncated cone-shaped, or even diamond-shaped.
The color of cashews varies from pale yellow to bright red and may have green patches on the surface.
The color of cashews varies from pale yellow to bright red and may have green patches on the surface.
External shell
The outer shell of the cashew fruit is a thin, gray or brown layer.
When the cashew fruit is ripe, the outer shell opens and reveals the seed inside. This outer shell is usually hard and inedible.
When the cashew fruit is ripe, the outer shell opens and reveals the seed inside. This outer shell is usually hard and inedible.
Cashew nuts
This is an important part of the cashew fruit.
Cashew nuts are shaped like chestnuts, but larger. They are usually white or pale and have a sweet, sour, and astringent taste.
Cashew nuts are rich in nutrients, including protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
Cashew nuts are shaped like chestnuts, but larger. They are usually white or pale and have a sweet, sour, and astringent taste.
Cashew nuts are rich in nutrients, including protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
Uses
Cashews are commonly eaten fresh, roasted, or used as a spice in various dishes.

Enjoy your experience of enjoying cashews!
The difference between cashews and other nutritious nuts
Cashews are a type of nut rich in monounsaturated fats, with many health benefits. Here is a detailed description of cashews and a comparison with some other nutritious nuts:
Cashews
Origin: Cashews, also known as cashews, are native to South America, especially northeastern Brazil. Currently, cashews are grown in many provinces in Vietnam.
Nutrition content: Cashews contain many nutrients, including magnesium, fiber, protein, vitamin E, and monounsaturated fatty acids. Cashews also have the ability to reduce depression and protect the retina from the effects of UV1 rays.
Cashews are shaped like chestnuts, but larger.
The color of cashews varies from light yellow to bright red.
Contains many nutrients such as protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
Nutrition content: Cashews contain many nutrients, including magnesium, fiber, protein, vitamin E, and monounsaturated fatty acids. Cashews also have the ability to reduce depression and protect the retina from the effects of UV1 rays.
Cashews are shaped like chestnuts, but larger.
The color of cashews varies from light yellow to bright red.
Contains many nutrients such as protein, fat, vitamins, and minerals.
Sesame Seeds
Origin: Sesame seeds are native to Africa and are widely grown in tropical and subtropical regions, especially Asia.
Special Features: Sesame seeds are commonly used in cooking and have a strong flavor. They are also rich in nutrients, including calcium, magnesium, iron, fiber, vitamin E, and vitamin B6.
Commonly used in dishes and confectionery.
Special Features: Sesame seeds are commonly used in cooking and have a strong flavor. They are also rich in nutrients, including calcium, magnesium, iron, fiber, vitamin E, and vitamin B6.
Commonly used in dishes and confectionery.

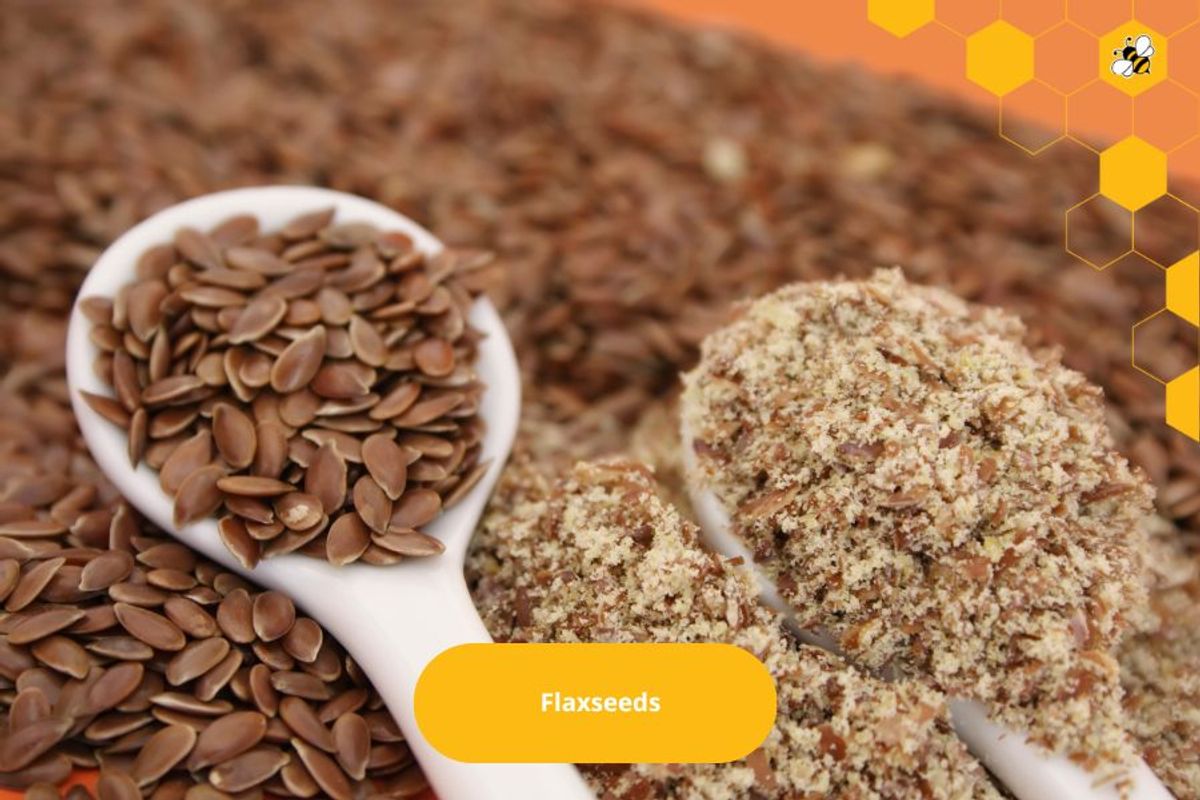
Flaxseeds
Origin: Flaxseeds are native to the Middle East and are imported for processing and sale across the country.
Special features: Flaxseeds contain fiber, omega-3, lignans, calcium, and protein. They can lower cholesterol and support the cardiovascular system.
Commonly used to make flaxseed flour, add to drinks, or spread on bread.
Special features: Flaxseeds contain fiber, omega-3, lignans, calcium, and protein. They can lower cholesterol and support the cardiovascular system.
Commonly used to make flaxseed flour, add to drinks, or spread on bread.
Brazil Nuts
Origin: Brazil nuts are native to South America, especially northeastern Brazil, and are grown in many countries.
Special Features: Brazil nuts contain selenium, vitamin E, magnesium, fiber, and a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage.
Usually eaten fresh or roasted.
Special Features: Brazil nuts contain selenium, vitamin E, magnesium, fiber, and a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage.
Usually eaten fresh or roasted.

Cacao beans
The seeds of the cacao tree, native to Central America.
Contains flavonoids, antioxidants, and fiber.
Used to make chocolate and cocoa products.
Contains flavonoids, antioxidants, and fiber.
Used to make chocolate and cocoa products.

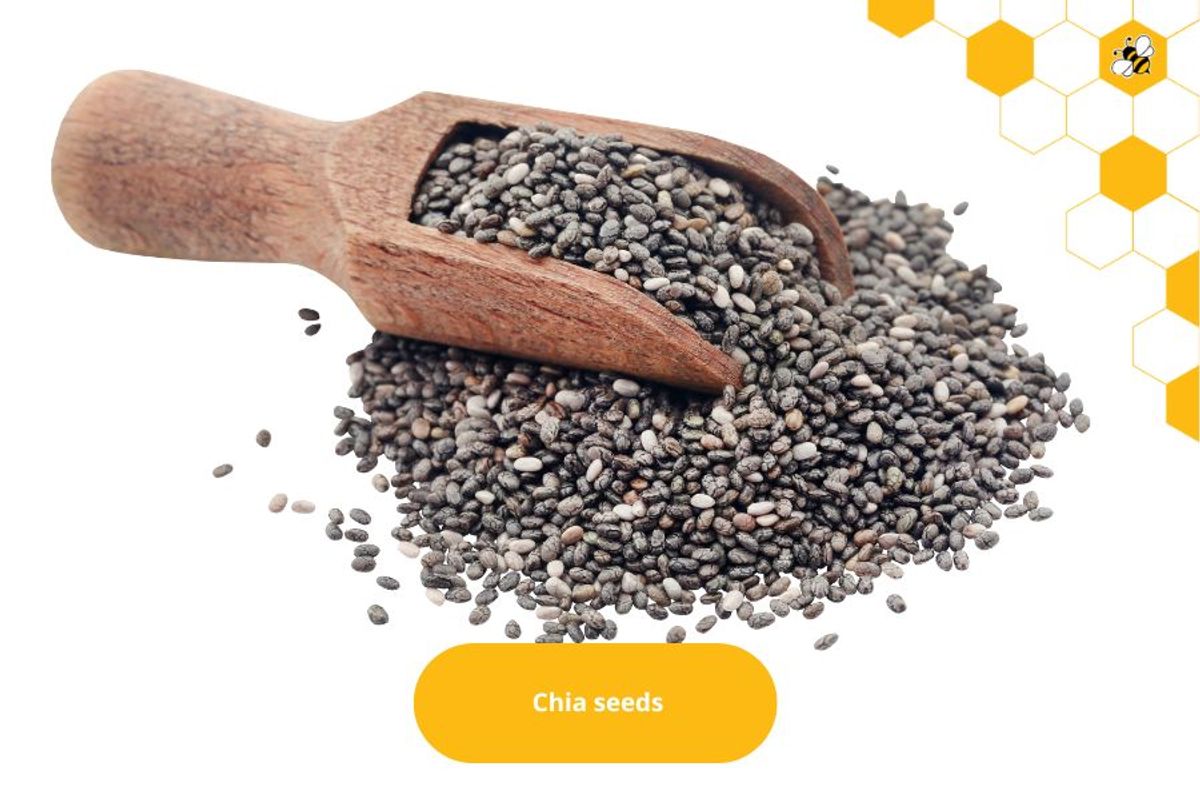
Chia seeds
Originally from Mexico and Guatemala.
High in fiber, omega-3, protein, and calcium.
Usually soaked in water and used in dishes.
Remember to incorporate these seeds into your daily diet to ensure adequate fat and nutrition for your body.
High in fiber, omega-3, protein, and calcium.
Usually soaked in water and used in dishes.
Remember to incorporate these seeds into your daily diet to ensure adequate fat and nutrition for your body.
Summary
The above article has just introduced to everyone the full and detailed characteristics of cashew nuts. Hopefully, it can bring everyone useful information in identifying and distinguishing cashew nuts, as well as the difference between cashew nuts and other nutritious nuts on the market.